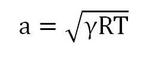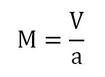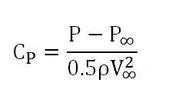CFD-Post Built in Functions
Some examples on how to use the built in functions in CFD Post data analysis.
Example
Coding the speed of sound into CFX.
Example
Coding the Mach number into CFX.
Example
Coding the specific pressure coefficient
Calculating Nusselt Number
Remember you have a solid domain and a fluid domain. The solid domain is to calculate the conductive heat flux, the fluid domain is to calculate the convective heat flux. The ratio of both fluxes are the Nusselt number.
You will need to assign a named surface for the selected areas of the fin of interest. That will be done in the meshing part of the project. Right click on the background after selecting the surfaces of interest.
In CFD post select the named surface and use the ready function provided by CFX such as calculating the average value of a scalar (heat flux) for a selected surface, that is from the fluid domain side:
You will need to assign a named surface for the selected areas of the fin of interest. That will be done in the meshing part of the project. Right click on the background after selecting the surfaces of interest.
In CFD post select the named surface and use the ready function provided by CFX such as calculating the average value of a scalar (heat flux) for a selected surface, that is from the fluid domain side:
Numerical Functions and Operators
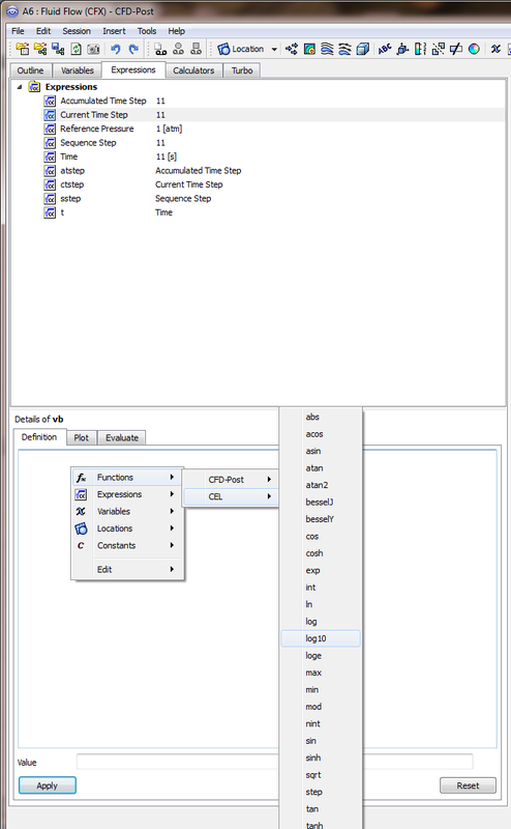
The use of numerical functions comes when the researcher gets to the analysis stage, and uses different provided functions in order to validate that his produced data is the same as experimental data. As can be seen in the following figure is that you can insert the function in the expressions section by applying a new expression and assigning a name to it, then by right click in the details section of the expression you get to select the required mathematical function.
Measuring Concentration at a Point in a Domain
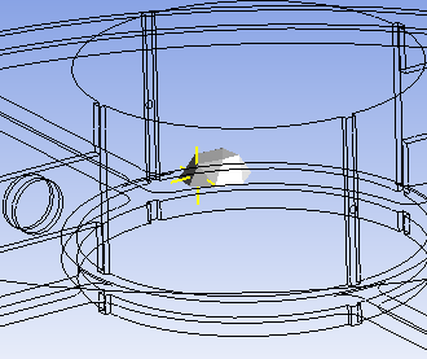
The following figure shows the volume Node located near the point of study in order to calculate concentration.
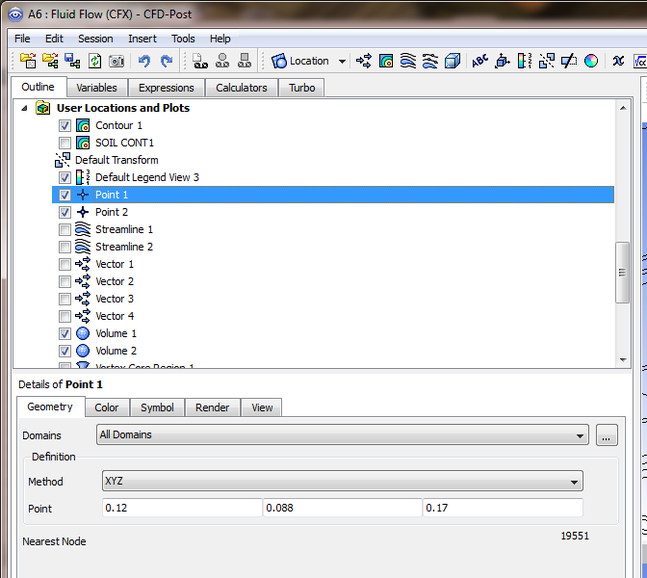
1-Insert point1 and save the coordinates values on a note pad or jot the numbers down on a paper, under the coordinates window is the Nearest Node option which gives you the number of the Nearest Node.
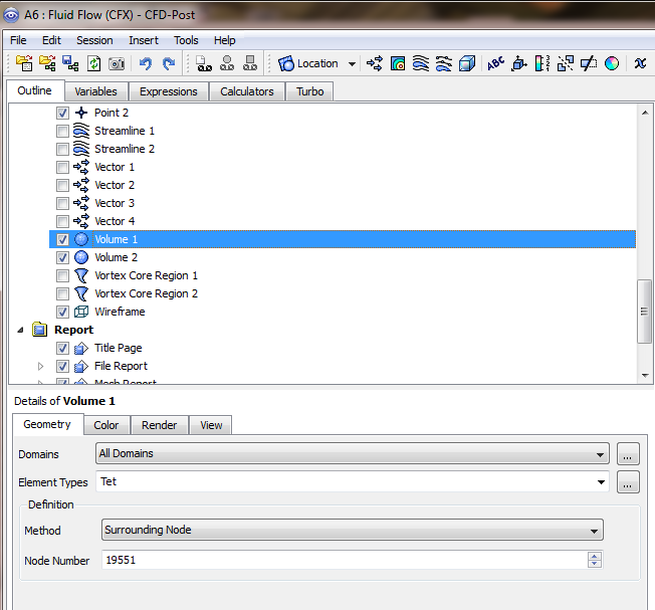
2-Insert a volume into the domain, choose under Elments Types: Tet, then under the definition section choice under method Surrounding Node option and apply the Node number closest to the point of insert.
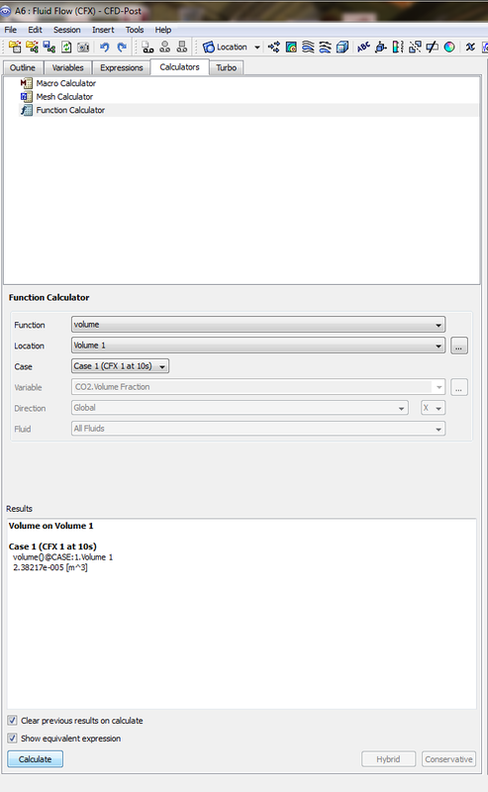
3-Then comes the calculation of the volume of the indicated Node number, through the built in functions.
Finding Species Concentration at a Point
This tutorial was written by Ahmed Al Makky to answer the regular question of how to find the concentration of a gas species using known volume fractions.
Unless otherwise noted, all content on this site is @Copyright by Ahmed Al Makky 2012-2014 - http://cfd2012.com