VERY IMPORTANT Guide Lines for PhD Students to What Research Area to Choose when Thinking of Working in the Field of Computational Fluid Dynamics:
Once you get through these points you can get a clear picture in which area you want to work in.
A-You can choose to work either on ready Computational Fluid Dynamics packages:
These software packages are ANSYS-CFX, ANSYS-FLUENT, STAR-CCM+, ANSYS Mechanical, ANSYS PolyFlow, ANSYS Offshore, ANSYS Explicit, ........ etc. It all depends on what problem will you be trying to solve during your PhD. It is a requirement for the supervisor to have knowledge about the software the student is going to use. This is because from there he can verify if the software can solve the problem and that the computer hardware available at the faculty is enough to conduct calculations that achieve the projects goals. Off course your supervisor at some point can't give you any assistance because these software's are complex, not easy to learn and are developing very fast. It won't be helpful in going to online forums and the user's manual provided by the company. These materials are made for people who have taken training courses and need to refresh what they have done before. At that point you would require a training course, these courses are expensive and are provided by the companies that make these kinds of software. Therefore in addition to paying the university fees it is also required to have a budget for the training courses. It is required to have a research group to work with. Because these software packages are formed of several software's each for a specified purpose. This area is preferable for engineering background students, because the researcher will be using the interface tools provided with the software. These interface tools will help him in generating his meshed geometry, to choose the numerical solution model, to choose what kind of flow case is studied flow (Subsonic, Sonic, Supersonic, Ultrasonic) to select the.
B-You can choose to work on Computational Fluid Dynamics models development:
To work in the field of models development then you would require a strong back ground in Programming, Numerical Analysis, Linear Algebra, Algorithms, Computational PDEs including, Code Parallelization, Statistics and Probability. Without this foundation the student would not be able to get anywhere, because the complexity of the problems he will face will be too difficult to solve in the PhD required period. In addition to the need to have a team of researchers in the group to help you out when you do get stuck. If a bug doesn't get solved no way you can get to the upgrade panel with results. This area is preferable to mathematicians and physicists and computer science researchers, not at all recommended to engineering students. This kind of project can be implemented on computer resources and software that are less costly than using the commercial codes. You can even acquire the required skills before you start your PhD through using OpenFoam while software's like ANSYS and STAR-CCM+ once you have no access to the software you won't be able to develop your skills using them.
C-You can choose to work on the development of Computational Fluid Dynamics packages:
This area would require the student to be a mathematician who has good knowledge in programming or a computer science scientist. This kind of project would be directly involved with the software company.
A-You can choose to work either on ready Computational Fluid Dynamics packages:
These software packages are ANSYS-CFX, ANSYS-FLUENT, STAR-CCM+, ANSYS Mechanical, ANSYS PolyFlow, ANSYS Offshore, ANSYS Explicit, ........ etc. It all depends on what problem will you be trying to solve during your PhD. It is a requirement for the supervisor to have knowledge about the software the student is going to use. This is because from there he can verify if the software can solve the problem and that the computer hardware available at the faculty is enough to conduct calculations that achieve the projects goals. Off course your supervisor at some point can't give you any assistance because these software's are complex, not easy to learn and are developing very fast. It won't be helpful in going to online forums and the user's manual provided by the company. These materials are made for people who have taken training courses and need to refresh what they have done before. At that point you would require a training course, these courses are expensive and are provided by the companies that make these kinds of software. Therefore in addition to paying the university fees it is also required to have a budget for the training courses. It is required to have a research group to work with. Because these software packages are formed of several software's each for a specified purpose. This area is preferable for engineering background students, because the researcher will be using the interface tools provided with the software. These interface tools will help him in generating his meshed geometry, to choose the numerical solution model, to choose what kind of flow case is studied flow (Subsonic, Sonic, Supersonic, Ultrasonic) to select the.
B-You can choose to work on Computational Fluid Dynamics models development:
To work in the field of models development then you would require a strong back ground in Programming, Numerical Analysis, Linear Algebra, Algorithms, Computational PDEs including, Code Parallelization, Statistics and Probability. Without this foundation the student would not be able to get anywhere, because the complexity of the problems he will face will be too difficult to solve in the PhD required period. In addition to the need to have a team of researchers in the group to help you out when you do get stuck. If a bug doesn't get solved no way you can get to the upgrade panel with results. This area is preferable to mathematicians and physicists and computer science researchers, not at all recommended to engineering students. This kind of project can be implemented on computer resources and software that are less costly than using the commercial codes. You can even acquire the required skills before you start your PhD through using OpenFoam while software's like ANSYS and STAR-CCM+ once you have no access to the software you won't be able to develop your skills using them.
C-You can choose to work on the development of Computational Fluid Dynamics packages:
This area would require the student to be a mathematician who has good knowledge in programming or a computer science scientist. This kind of project would be directly involved with the software company.
University Department Links that are Involved in CFD Research
The following links are of research groups conducting research in the field of computational fluid dynamics.
1-Labrotary for Aero and Hydrodynamics TUDelft
2-Stanford University Research Projects
3-Stanford University Researcher Website Associate Professor Ron Fedkiw.
4-KTH Library Publication Database.
5-The Department of Applied Mechanics Sweeden.
6-Advanced Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Tokyo Institute of Technology.
7-Stanford Flow Physics and Computational Engineeriing (FPCE Group).
8-International Workshop On Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Premixed Flames.
9-The Web Site of Professor Lars Davidson , Division of Fluid Mechanics Goteborg Sweden.
1-Labrotary for Aero and Hydrodynamics TUDelft
2-Stanford University Research Projects
3-Stanford University Researcher Website Associate Professor Ron Fedkiw.
4-KTH Library Publication Database.
5-The Department of Applied Mechanics Sweeden.
6-Advanced Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Tokyo Institute of Technology.
7-Stanford Flow Physics and Computational Engineeriing (FPCE Group).
8-International Workshop On Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Premixed Flames.
9-The Web Site of Professor Lars Davidson , Division of Fluid Mechanics Goteborg Sweden.
Initial Steps for the Researchers to Follow:
CFD projects are big projects for research and PhD students. Research projects require problem solving skills which you either have before or you need to gain with time. These kind of projects may take the researcher at least six months to build and calibrate the simulations to get the required results. Usually these projects are split into different stages to build the numerical model using the interface tools provided by the software. The majority of new researchers lack the back ground needed but such a project needs:
1-guidance provided to you through the group you are working with or through your supervisor.
2-If your research group cannot assist you then you can ask a researcher at your university, if not ask some at another university near where you live, if not ask someone on the net.
3-You can bypass your problems by asking your boss to back you up for a training course with ANSYS CFX.
4-You can contact ANSYS for any enquirers, if your research institute has the software and is currently using it, they will be happy to answer you quires I have contacted them several times.
1-guidance provided to you through the group you are working with or through your supervisor.
2-If your research group cannot assist you then you can ask a researcher at your university, if not ask some at another university near where you live, if not ask someone on the net.
3-You can bypass your problems by asking your boss to back you up for a training course with ANSYS CFX.
4-You can contact ANSYS for any enquirers, if your research institute has the software and is currently using it, they will be happy to answer you quires I have contacted them several times.
Steps Required to Understand a Given CFD Code
The following steps can simplify the confusing process of reading a given code:
1- Print out the code.
2- Get a folder and separate the written sub-routines into chapters in the folder.
3- Draw a flow chart for each subroutine.
4- Draw a flow chart for the Main program.
5- Define the parameters written in the input file. Write them into a table and on another column write its definition.
6- Start reading each routine and try to find the used variables in the code, these are defined constants, and variables. Write them into a table and on another column write its definition.
7- Pick out the used matrices in the code and do the same thing, Write them into a table and on another column write its purpose of use.
8- Then comes seeing if there are any called functions, Write them into a table and on another column write its purpose of use.
9- Once this is done try to see what equation or differential equation is being solved.
10- Try to find where is the data output written to, this is required for the data analysis stage of the project.
11- Try to write the description of each subroutine and what is happening inside the code.
12- You can separate each subroutine, try to assign the used variables the required values and see what data is generated from the subroutine.
13- Keep the folder beside you and update what you understand and learn throughout the learning process.
1- Print out the code.
2- Get a folder and separate the written sub-routines into chapters in the folder.
3- Draw a flow chart for each subroutine.
4- Draw a flow chart for the Main program.
5- Define the parameters written in the input file. Write them into a table and on another column write its definition.
6- Start reading each routine and try to find the used variables in the code, these are defined constants, and variables. Write them into a table and on another column write its definition.
7- Pick out the used matrices in the code and do the same thing, Write them into a table and on another column write its purpose of use.
8- Then comes seeing if there are any called functions, Write them into a table and on another column write its purpose of use.
9- Once this is done try to see what equation or differential equation is being solved.
10- Try to find where is the data output written to, this is required for the data analysis stage of the project.
11- Try to write the description of each subroutine and what is happening inside the code.
12- You can separate each subroutine, try to assign the used variables the required values and see what data is generated from the subroutine.
13- Keep the folder beside you and update what you understand and learn throughout the learning process.
Data Analysis:
Hope these steps are useful.
Stage 1:
Make a simple drawing of your studied case. Then specfiy your inflow and out flow regions. Imagine it just like a Lego buliding blocks. As a first step make a very simple simulation with just an inflow velocity and an openning as an outlet. Then once you clarfiy that the simulation runs and results can be produced then comes the addition of new varaibles. These values are usually standrad such as 1.29kg/m^3 density of air 300 K ambient temperature 1 atm for pressure.Then try to see in publications if some thing similar has been done and try to extract from it values that you can use for your case. If the case is in your experimental lab that can be a straight forward job. After a calculaion run had been done. Using the data visulization tools start plotting the data. Any research topic has several parameters that need to be studied to extract from them the occuring patterns. The supervisour would have given you a hint to them or would have asked you to extract them from published material. You will start releating these varaibles to gemetrical constraints or to thermodynamic varabiles. At the first instance save all the captured plots for the diffrent studied variabiles. Make print outs of these plots hang them on the wall and try relating the diffrent variables with diffrent plots. After a while you start seeing that for example gravitaional effects are dominant or bounacy effects temperature etc. Next write all of them in a list. Now that you have the list.
Stage 2:
From the first stage use the same list make your plots in accurate form giving the axis titles and plots titles. At this stage start trying to make your simulation mimic your studied case as an example if you where in real life getting water to boil at 100 deg try to make it achive the same value in the simulation. This is done nby playing around with the existing variables in your simulation.
once you start getting the feel of the effects of the diffrent variables thats when you can try to make your simulation look as real as possible.
Stage 3:
This represnts the final stage of analysis process. At this stage you will choose wether you will need to add any extra stuff or not.
Stage 1:
Make a simple drawing of your studied case. Then specfiy your inflow and out flow regions. Imagine it just like a Lego buliding blocks. As a first step make a very simple simulation with just an inflow velocity and an openning as an outlet. Then once you clarfiy that the simulation runs and results can be produced then comes the addition of new varaibles. These values are usually standrad such as 1.29kg/m^3 density of air 300 K ambient temperature 1 atm for pressure.Then try to see in publications if some thing similar has been done and try to extract from it values that you can use for your case. If the case is in your experimental lab that can be a straight forward job. After a calculaion run had been done. Using the data visulization tools start plotting the data. Any research topic has several parameters that need to be studied to extract from them the occuring patterns. The supervisour would have given you a hint to them or would have asked you to extract them from published material. You will start releating these varaibles to gemetrical constraints or to thermodynamic varabiles. At the first instance save all the captured plots for the diffrent studied variabiles. Make print outs of these plots hang them on the wall and try relating the diffrent variables with diffrent plots. After a while you start seeing that for example gravitaional effects are dominant or bounacy effects temperature etc. Next write all of them in a list. Now that you have the list.
Stage 2:
From the first stage use the same list make your plots in accurate form giving the axis titles and plots titles. At this stage start trying to make your simulation mimic your studied case as an example if you where in real life getting water to boil at 100 deg try to make it achive the same value in the simulation. This is done nby playing around with the existing variables in your simulation.
once you start getting the feel of the effects of the diffrent variables thats when you can try to make your simulation look as real as possible.
Stage 3:
This represnts the final stage of analysis process. At this stage you will choose wether you will need to add any extra stuff or not.
Check List when Expected Simulation Data is Not Obtained:
1- Check the used model equations.
2- Next comes look at each part of the used equations and see their impact on the results.
3- Then see the required input parameters for the constants.
4- Check at what level of length scales are you intrested in milliscopic,macroscopic,microscopic this can give you hints.
2- Next comes look at each part of the used equations and see their impact on the results.
3- Then see the required input parameters for the constants.
4- Check at what level of length scales are you intrested in milliscopic,macroscopic,microscopic this can give you hints.
What is the Sceintfic Contribution of the CFD Project?
A scientific contribution of a CFD project is
anything which adds to the knowledge of mentioned field of science or the
number of things that can be achieved by the introduction of a new mathematical
tool. It might be a discovery, a new theorem or an innovative application of
existing knowledge. The example of an innovation application of an existing
knowledge is the use the momentum statistical method and applying it to
Turbulence modelling. Another innovation is the use of probability distribution
function in the development of Turbulence models. Due to that turbulence
involves lots of statistics and random motion of particles some have gone to
the extent of adopting methods used in times series analysis and signal
processing. Other
have opted on applying statistical tools for
producing much better data.
CFD uses mathematical tools that have been developed for differential equations to solve the Navier Stokes Equations to find a new inovation in that area as an example you will need to find a new mathematical method being used to solve differential equations and hasnt been applied yet by CFD researchers that will result of you being the first to do that work.
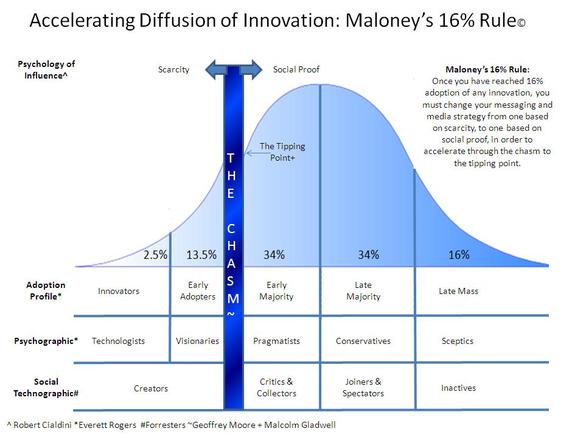
Diffusion of Innovation
Once innovation occurs, innovations may be spread from the innovator to other individuals and groups.This a pattern you will see This process has been proposed that the life cycle of innovations can be described using the S curve (image taken from the following link, it is not done by me). The S part of the curve is represented in the region of Adoption Profile to the social Proof.
A scientist called Gabriel Tarde defined the innovation-decision process as a series of steps I have applied them for the case of computational fluid dynamics.
1- First knowledge of the numerical method.
2- Forming an attitude and applying the mathematical tool to the problem.
3- A decision to adopt or reject based on seeing how easy and straight forward it is, that based on seeing is it taught in general mathematics text books, do lots researchers in the applied mathematics field faviour the method or do they see it to complex to work with.
4- Implementation and use, trials in solving the problem for a standard case then seeing how the new tools performs while used on new application of intrest.
5- Confirmation of the decision is based on seeing how practical the idea is, as an example the method might require less computer resources than the usuall.
2- Forming an attitude and applying the mathematical tool to the problem.
3- A decision to adopt or reject based on seeing how easy and straight forward it is, that based on seeing is it taught in general mathematics text books, do lots researchers in the applied mathematics field faviour the method or do they see it to complex to work with.
4- Implementation and use, trials in solving the problem for a standard case then seeing how the new tools performs while used on new application of intrest.
5- Confirmation of the decision is based on seeing how practical the idea is, as an example the method might require less computer resources than the usuall.
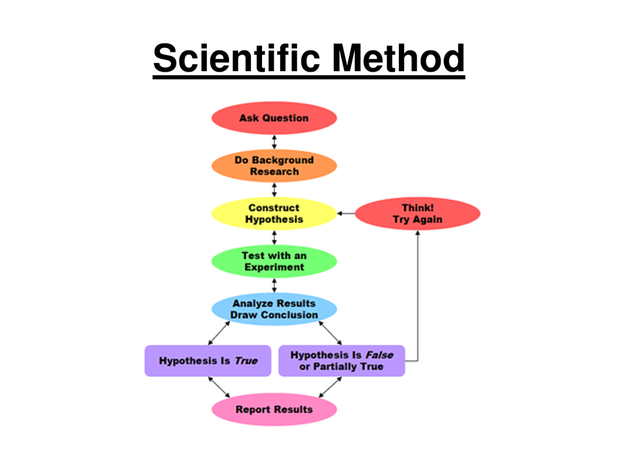
Scientific Method
Talking from the prespective of an engineer that has shiffted his intrest to an area of applied physics. He will be familiar with the Engineering Design Process Method but will find him that he needs to get exposed to the Scientific Method. There are some differences between the two methods
The following link is recommended:
http://www.sciencebuddies.org/engineering-design-process/engineering-design-compare-scientific-method.shtml
The following link is recommended:
http://www.sciencebuddies.org/engineering-design-process/engineering-design-compare-scientific-method.shtml
Questions that you Ask your Self to Asses your CFD Work
The following points can form a check list to to go through during your write up period of your thesis and during the preperation process before your viva, these steps can also be used as a check list during your write up a researcher paper.
1- What is the sceintific contribution of the written material to the field of CFD?
2- How relevant is this material to the scop of your research area.
3- How novel is the described research? are you aware of any related produced work? this should be clear to the researcher after writting his litrature review in relation to what research has been done and what mathematical tools had been used.
4- How significant is the described research? the importance and significance of the work comes on how much human society needs the innovation and dose the idea seem to have a future prespective and contribution to man kind.
5- Is the research technically sound, has the numerial method been tested and proven to have small error that occours in resonable ranges? Thats why you will see publications comparing between diffrent numerical used models and experimental data.
6- Do I describe the limitaions of the approach in a satisfactory manner?
7- Dose the title of the work clearly and sufficiently reflects its contents?
8- Are the refererances adequat and are they all neceessary.
9- Are the key words and abstract/summary infromative.
10- Is the material,organization and length satisfactory.
11- Can i suggest additions or amendments or an introductory statment that will increase the value of the material?
12- Are the illustrations and tabels necessary and acceptable?
13- To what extent dose the material fall whithin your area of expertise?
14- Can i suggest any reduction in the material, or deletions of parts?
15- Is the material acceptable to be shared in its present form?
Is the material acceptable after minor revisions are made to it?
Is the material acceptable for sharing after major revisions are made to it?
Is the material unaccepatble to be shared even with major revisions are conducted?
The lack of theoretical justfication of the proposed personalisation approach.
The evaluation procedure and results.
The presentation of the learning environment and its innovative characterstics.
1- What is the sceintific contribution of the written material to the field of CFD?
2- How relevant is this material to the scop of your research area.
3- How novel is the described research? are you aware of any related produced work? this should be clear to the researcher after writting his litrature review in relation to what research has been done and what mathematical tools had been used.
4- How significant is the described research? the importance and significance of the work comes on how much human society needs the innovation and dose the idea seem to have a future prespective and contribution to man kind.
5- Is the research technically sound, has the numerial method been tested and proven to have small error that occours in resonable ranges? Thats why you will see publications comparing between diffrent numerical used models and experimental data.
6- Do I describe the limitaions of the approach in a satisfactory manner?
7- Dose the title of the work clearly and sufficiently reflects its contents?
8- Are the refererances adequat and are they all neceessary.
9- Are the key words and abstract/summary infromative.
10- Is the material,organization and length satisfactory.
11- Can i suggest additions or amendments or an introductory statment that will increase the value of the material?
12- Are the illustrations and tabels necessary and acceptable?
13- To what extent dose the material fall whithin your area of expertise?
14- Can i suggest any reduction in the material, or deletions of parts?
15- Is the material acceptable to be shared in its present form?
Is the material acceptable after minor revisions are made to it?
Is the material acceptable for sharing after major revisions are made to it?
Is the material unaccepatble to be shared even with major revisions are conducted?
The lack of theoretical justfication of the proposed personalisation approach.
The evaluation procedure and results.
The presentation of the learning environment and its innovative characterstics.
Unless otherwise noted, all content on this site is @Copyright by Ahmed Al Makky 2012-2015 - http://cfd2012.com