Example Using Matlab Interface Tools GUI
To make an interface has to have a staged approach, by asking my self is it worth the effort?
Once the objective is specified,the objective means do i want the interface just to view data, do i want to view 2D or 3D or do i want both at the same time, .....etc, do i need to change any values during the process, do i need to view some values while a simulation is run .
Next comes, making your self familer with the provided function in Matlab.
Making a quick drawing of your interface help out in knowing how many buttons are needed , and how many plots are required..... etc.
The researcher finds that their are primary aims of some buttons to use and ther are secondary aims. what is meant by primary is that the interface cant accomplish its task with thought them, secondary aims means that the interface satisfies its required goals with or without the buttons.
Examples of a visualizations interface:
clear, clc, pause,.... etc, are secondary commands
plot, contour, Meshgrid, .....etc ,are primary commands.
Using GUI just as a simple example for getting a a button menu:
This created menu has four buttons the first two buttons produce matricies of 5 or 10 cells, the thrid and fourth button makes to matrcies and stories them in an independent matrix b.
Adding buttons to the figure that help out in visualizations:
Making Calculator Interface:
http://www.intelligent-systems.info/classes/ee509/gui.htm
Using matlab interface.
Once the objective is specified,the objective means do i want the interface just to view data, do i want to view 2D or 3D or do i want both at the same time, .....etc, do i need to change any values during the process, do i need to view some values while a simulation is run .
Next comes, making your self familer with the provided function in Matlab.
Making a quick drawing of your interface help out in knowing how many buttons are needed , and how many plots are required..... etc.
The researcher finds that their are primary aims of some buttons to use and ther are secondary aims. what is meant by primary is that the interface cant accomplish its task with thought them, secondary aims means that the interface satisfies its required goals with or without the buttons.
Examples of a visualizations interface:
clear, clc, pause,.... etc, are secondary commands
plot, contour, Meshgrid, .....etc ,are primary commands.
Using GUI just as a simple example for getting a a button menu:
This created menu has four buttons the first two buttons produce matricies of 5 or 10 cells, the thrid and fourth button makes to matrcies and stories them in an independent matrix b.
Adding buttons to the figure that help out in visualizations:
Making Calculator Interface:
http://www.intelligent-systems.info/classes/ee509/gui.htm
Using matlab interface.
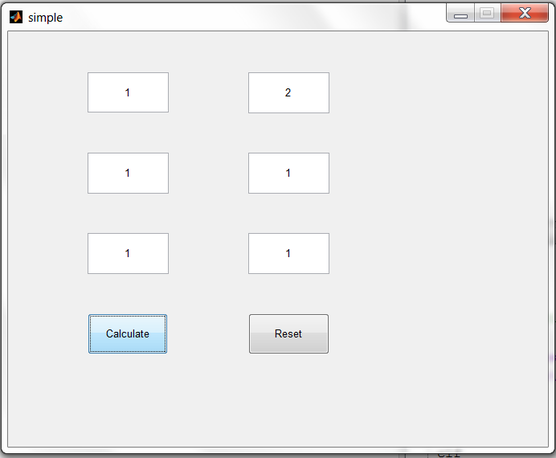
Example Using GUI for Simple Algebric Operations
function varargout = simple(varargin)
% SIMPLE MATLAB code for simple.fig
% SIMPLE, by itself, creates a new SIMPLE or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = SIMPLE returns the handle to a new SIMPLE or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% SIMPLE('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in SIMPLE.M with the given input arguments.
%
% SIMPLE('Property','Value',...) creates a new SIMPLE or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before simple_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to simple_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help simple
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 28-Jan-2013 10:37:58
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @simple_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @simple_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before simple is made visible.
function simple_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to simple (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for simple
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes simple wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = simple_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function input1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input1 as a double
a = get(hObject,'String');
handles.a=a;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input2 as a double
b = get(hObject,'String');
handles.b=b;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input3 as a double
c = get(hObject,'String');
handles.c=c;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function out1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of out1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of out1 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function out1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function out2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of out2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of out2 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function out2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function out3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of out3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of out3 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function out3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a = get(handles.input1,'String');
b = get(handles.input2,'String');
c = get(handles.input3,'String');
aa=2*str2num(a);
bb=str2num(a)*str2num(b);
cc=str2num(a)/str2num(b);
set(handles.out1,'String',aa);
set(handles.out2,'String',bb);
set(handles.out3,'String',cc);
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a = get(handles.input1,'String');
b = get(handles.input2,'String');
c = get(handles.input3,'String');
set(handles.input1,'String',0);
set(handles.input2,'String',0);
set(handles.input3,'String',0);
set(handles.out1,'String',0);
set(handles.out2,'String',0);
set(handles.out3,'String',0);
clc
guidata(hObject,handles);
% SIMPLE MATLAB code for simple.fig
% SIMPLE, by itself, creates a new SIMPLE or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = SIMPLE returns the handle to a new SIMPLE or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% SIMPLE('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in SIMPLE.M with the given input arguments.
%
% SIMPLE('Property','Value',...) creates a new SIMPLE or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before simple_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to simple_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help simple
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 28-Jan-2013 10:37:58
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @simple_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @simple_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before simple is made visible.
function simple_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to simple (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for simple
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes simple wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = simple_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function input1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input1 as a double
a = get(hObject,'String');
handles.a=a;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input2 as a double
b = get(hObject,'String');
handles.b=b;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input3 as a double
c = get(hObject,'String');
handles.c=c;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function out1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of out1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of out1 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function out1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function out2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of out2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of out2 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function out2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function out3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of out3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of out3 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function out3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to out3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a = get(handles.input1,'String');
b = get(handles.input2,'String');
c = get(handles.input3,'String');
aa=2*str2num(a);
bb=str2num(a)*str2num(b);
cc=str2num(a)/str2num(b);
set(handles.out1,'String',aa);
set(handles.out2,'String',bb);
set(handles.out3,'String',cc);
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a = get(handles.input1,'String');
b = get(handles.input2,'String');
c = get(handles.input3,'String');
set(handles.input1,'String',0);
set(handles.input2,'String',0);
set(handles.input3,'String',0);
set(handles.out1,'String',0);
set(handles.out2,'String',0);
set(handles.out3,'String',0);
clc
guidata(hObject,handles);
Example GUI Message Box
The simplest command to use is this:
msgbox('Wrong Input Value'), this can be used for conditional statements input condition. While for a more complex case if you want what inputed into the cell to be given back in the message window then type the following command
msgbox(get(hObject,'String'))
If you have an input cell by knowing whats its name:
Val=str2num(get(handles.editinput,'string'))
msgbox(num2str(val))
Some Hints:
a=str2num(get(handles.a,'string'))
b=str2num(get(handles.b,'string'))
c=str2num(get(handles.c,'string'))
int=num2str(c/b);
slope=num2str(-a/b);
set(handles.y,'string',int);
set(handles.slope,'string',slope);
x=0:10;
y=c/b-a/b*x;
axes(handles.axes1)
plot(x,y);
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
guidata(hObject.handles)
Some useful links:
1-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pPcaxvPUtBg
2-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I-JP24_VF58
3-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u06LwtHIh6Q
4-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=60zHJ1sEFhQ
5-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D_hmws6dwgg
6-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KPQZzPp03Rg
Summary:
some cells are required for input, you need to tag them with a name so that you can call them through the call back function. Remmber that the values need to be read in and then stored to be recalled during other needed operations, therefore these cells will need to be first assigned a value by the user and then the user has to press a button. Meaning a button needs to be made that has a call back function to read the values in the input cells. The user has to go to the call back function for the created button and use a command to read in the required values as an example the following
get(handles.input1,'String');
There will be a need at some point to perform some algebric operations therefore it is required to assign the command to a string
A1 = get(handles.input1,'String');
This is still the first step, if the user types into MATLAB A1 he will get zero. The next step is to use the following command str2num(A1) this will inturn enable the user to perform algebric operations becouse matlab will interpert A1 to a value.
So the cell is regarded after being added as a function input1_callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
input1=str2double(get(hObject,'strin'))
The majority of studied cases there is a need use a conditional statement to get the correct the input parameters
if isnan(input)
set(hObject,'string',0);
errordlg('Input must be a number','Error');
end
handles.metricdata.input1=input1;
guidata(hObject,handles)
Next comes using a calculate button :
function calculate_Callback(hObject,eventdata,handles)
mass=handles.inpu1*handles.input2
set(handles.mass,'String',mass)
Some options to change the unit texts, so by selecting, this function checks the selected option once this is selected the following commands are implmented.
function xx_SelectionChangeFcn(hObject, eventdata,handles)
if (hObject == handles.english)
set(handles.text4, 'String','Kg');
set(handles.text5, 'String','m');
set(handles.text6, 'String','N');
else
set(handles.text4, 'String','Ib');
set(handles.text4, 'String','foot');
set(handles.text4, 'String','Kg');
end
There is always a need to reset the values for the gui window to allow another calculation to be done:
function initialize_gui(fig_handle, handles,isreset)
if isfield(handles,'metricdata') && ~isreset
return;
end
handles.metricdata.density=0;
handles.metricdata.volume=0;
set(handles.density, 'string', handles.metricdata.density);
set(handles.volume, 'string', handles.metricdata.volume);
set(handles.mass, 'string', 0);
set(handles.text6, 'string', 'N');
set(handles.text4, 'string', 'kg');
set(handles.text5, 'string', m');
set(handles.text6, 'string', 'N');
guidata(handles.figure1, handles)
msgbox('Wrong Input Value'), this can be used for conditional statements input condition. While for a more complex case if you want what inputed into the cell to be given back in the message window then type the following command
msgbox(get(hObject,'String'))
If you have an input cell by knowing whats its name:
Val=str2num(get(handles.editinput,'string'))
msgbox(num2str(val))
Some Hints:
a=str2num(get(handles.a,'string'))
b=str2num(get(handles.b,'string'))
c=str2num(get(handles.c,'string'))
int=num2str(c/b);
slope=num2str(-a/b);
set(handles.y,'string',int);
set(handles.slope,'string',slope);
x=0:10;
y=c/b-a/b*x;
axes(handles.axes1)
plot(x,y);
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
guidata(hObject.handles)
Some useful links:
1-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pPcaxvPUtBg
2-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I-JP24_VF58
3-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u06LwtHIh6Q
4-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=60zHJ1sEFhQ
5-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D_hmws6dwgg
6-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KPQZzPp03Rg
Summary:
some cells are required for input, you need to tag them with a name so that you can call them through the call back function. Remmber that the values need to be read in and then stored to be recalled during other needed operations, therefore these cells will need to be first assigned a value by the user and then the user has to press a button. Meaning a button needs to be made that has a call back function to read the values in the input cells. The user has to go to the call back function for the created button and use a command to read in the required values as an example the following
get(handles.input1,'String');
There will be a need at some point to perform some algebric operations therefore it is required to assign the command to a string
A1 = get(handles.input1,'String');
This is still the first step, if the user types into MATLAB A1 he will get zero. The next step is to use the following command str2num(A1) this will inturn enable the user to perform algebric operations becouse matlab will interpert A1 to a value.
So the cell is regarded after being added as a function input1_callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
input1=str2double(get(hObject,'strin'))
The majority of studied cases there is a need use a conditional statement to get the correct the input parameters
if isnan(input)
set(hObject,'string',0);
errordlg('Input must be a number','Error');
end
handles.metricdata.input1=input1;
guidata(hObject,handles)
Next comes using a calculate button :
function calculate_Callback(hObject,eventdata,handles)
mass=handles.inpu1*handles.input2
set(handles.mass,'String',mass)
Some options to change the unit texts, so by selecting, this function checks the selected option once this is selected the following commands are implmented.
function xx_SelectionChangeFcn(hObject, eventdata,handles)
if (hObject == handles.english)
set(handles.text4, 'String','Kg');
set(handles.text5, 'String','m');
set(handles.text6, 'String','N');
else
set(handles.text4, 'String','Ib');
set(handles.text4, 'String','foot');
set(handles.text4, 'String','Kg');
end
There is always a need to reset the values for the gui window to allow another calculation to be done:
function initialize_gui(fig_handle, handles,isreset)
if isfield(handles,'metricdata') && ~isreset
return;
end
handles.metricdata.density=0;
handles.metricdata.volume=0;
set(handles.density, 'string', handles.metricdata.density);
set(handles.volume, 'string', handles.metricdata.volume);
set(handles.mass, 'string', 0);
set(handles.text6, 'string', 'N');
set(handles.text4, 'string', 'kg');
set(handles.text5, 'string', m');
set(handles.text6, 'string', 'N');
guidata(handles.figure1, handles)
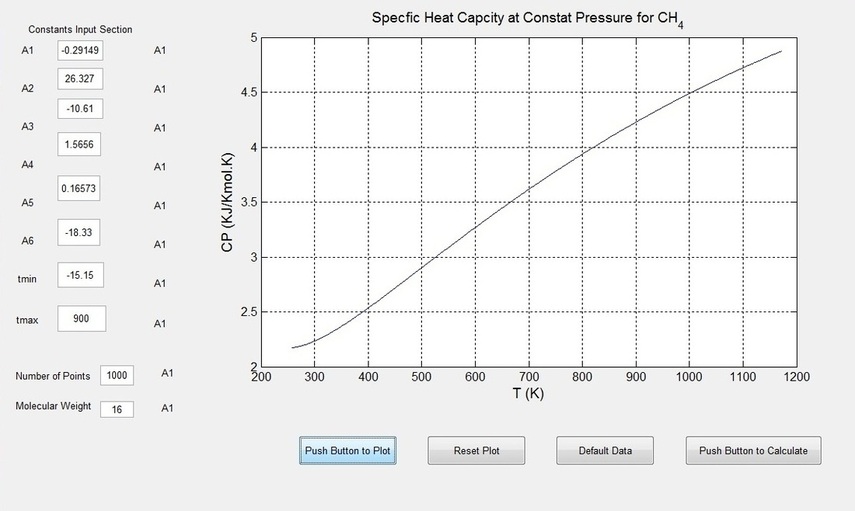
Example Using MATLAB GUI for Studing Methane Heat Capacity
function varargout = Methane(varargin)
% METHANE MATLAB code for Methane.fig
% METHANE, by itself, creates a new METHANE or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = METHANE returns the handle to a new METHANE or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% METHANE('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in METHANE.M with the given input arguments.
%
% METHANE('Property','Value',...) creates a new METHANE or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before Methane_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to Methane_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help Methane
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 26-Jan-2013 11:41:23
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @Methane_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @Methane_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before Methane is made visible.
function Methane_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to Methane (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for Methane
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes Methane wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = Methane_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function input1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input1 as a double
A1 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A1=A1
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input2 as a double
A2 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A2=A2
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input3 as a double
A3 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A3=A3
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input4 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input4 as a double
A4 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A4=A4
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input5 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input5 as a double
A5 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A5=A5
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input5_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input6 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input6 as a double
A6 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A6=A6
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input6_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input7 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input7 as a double
tMIN = get(hObject,'String');
handles.tMIN=tMIN
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input7_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input8 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input8 as a double
tMAX = get(hObject,'String');
handles.tMAX=tMAX
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input8_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input9 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input9 as a double
M = get(hObject,'String');
handles.M=M;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input9_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input10_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input10 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input10 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input10 as a double
Molecular_Weight = get(hObject,'String');
Molecular_Weight
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input10_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input10 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Access the globally stored data
CP=handles.CP
T=handles.T
plot(T,CP,'-')
grid on
xlabel('T (K)','FontSize',12)
ylabel('CP (KJ/Kmol.K)','FontSize',12)
%legend('Specfic Heat for CH_4')
title('Specfic Heat Capcity at Constat Pressure for CH_4','FontSize',12)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a = get(handles.input1,'String');
b = get(handles.input2,'String');
c = get(handles.input3,'String');
d = get(handles.input4,'String');
e = get(handles.input5,'String');
f = get(handles.input6,'String');
g = get(handles.input7,'String');
h = get(handles.input8,'String');
i = get(handles.input9,'String');
j = get(handles.input10,'String');
set(handles.input1,'String',0);
set(handles.input2,'String',0);
set(handles.input3,'String',0);
set(handles.input4,'String',0);
set(handles.input5,'String',0);
set(handles.input6,'String',0);
set(handles.input7,'String',0);
set(handles.input8,'String',0);
set(handles.input9,'String',0);
set(handles.input10,'String',0);
guidata(hObject, handles);
clc
clear
cla
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
A1 = get(handles.input1,'String');
A2 = get(handles.input2,'String');
A3 = get(handles.input3,'String');
A4 = get(handles.input4,'String');
A5 = get(handles.input5,'String');
A6 = get(handles.input6,'String');
tMIN = get(handles.input7,'String');
tMAX = get(handles.input8,'String');
M = get(handles.input9,'String');
Molecular_Weight = get(handles.input10,'String');
set(handles.input1,'String',-0.29149);
set(handles.input2,'String',26.327);
set(handles.input3,'String',-10.610);
set(handles.input4,'String',1.5656);
set(handles.input5,'String',0.16573);
set(handles.input6,'String',-18.33);
set(handles.input7,'String',-15.1500);
set(handles.input8,'String',900);
set(handles.input9,'String',1000);
set(handles.input10,'String',16);
guidata(hObject,handles)
TMIN=273+tMIN;
TMAX=273+tMAX;
dt=(TMAX-TMIN)/M;
Dt(1)=TMIN;
for i=1:M+1;
Dt(i+1)=Dt(i)+dt;
TH(i)=Dt(i+1)/1000;
CP(i)=4.184*(A1+A2*TH(i)+A3*(TH(i))^2+A4*(TH(i))^3+A5*(TH(i))^-2)/16;
end
T=(TMIN:dt:TMAX);
% Store the data in handles as a structure to be able to access it globally
% from other functions
handles.CP=CP;
handles.T=T;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
A1 = get(handles.input1,'String');
A2 = get(handles.input2,'String');
A3 = get(handles.input3,'String');
A4 = get(handles.input4,'String');
A5 = get(handles.input5,'String');
A6 = get(handles.input6,'String');
tMIN = get(handles.input7,'String');
tMAX = get(handles.input8,'String');
M = get(handles.input9,'String');
Molecular_Weight = get(handles.input10,'String');
TMIN=273+str2num(tMIN);
TMAX=273+str2num(tMAX);
dt=(TMAX-TMIN)/str2num(M);
Dt(1)=TMIN;
for i=1:str2num(M)+1;
Dt(i+1)=Dt(i)+dt;
TH(i)=Dt(i+1)/1000;
CP(i)=4.184*(str2num(A1)+str2num(A2)*TH(i)+str2num(A3)*(TH(i))^2+str2num(A4)*(TH(i))^3+str2num(A5)*(TH(i))^-2)/str2num(Molecular_Weight);
end
T=(TMIN:dt:TMAX);
handles.CP=CP;
handles.T=T;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% METHANE MATLAB code for Methane.fig
% METHANE, by itself, creates a new METHANE or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = METHANE returns the handle to a new METHANE or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% METHANE('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in METHANE.M with the given input arguments.
%
% METHANE('Property','Value',...) creates a new METHANE or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before Methane_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to Methane_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help Methane
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 26-Jan-2013 11:41:23
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @Methane_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @Methane_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before Methane is made visible.
function Methane_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to Methane (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for Methane
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes Methane wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = Methane_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function input1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input1 as a double
A1 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A1=A1
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input2 as a double
A2 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A2=A2
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input3 as a double
A3 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A3=A3
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input4 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input4 as a double
A4 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A4=A4
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input5 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input5 as a double
A5 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A5=A5
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input5_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input6 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input6 as a double
A6 = get(hObject,'String');
handles.A6=A6
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input6_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input7 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input7 as a double
tMIN = get(hObject,'String');
handles.tMIN=tMIN
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input7_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input8 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input8 as a double
tMAX = get(hObject,'String');
handles.tMAX=tMAX
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input8_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input9 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input9 as a double
M = get(hObject,'String');
handles.M=M;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input9_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function input10_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input10 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of input10 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of input10 as a double
Molecular_Weight = get(hObject,'String');
Molecular_Weight
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function input10_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to input10 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Access the globally stored data
CP=handles.CP
T=handles.T
plot(T,CP,'-')
grid on
xlabel('T (K)','FontSize',12)
ylabel('CP (KJ/Kmol.K)','FontSize',12)
%legend('Specfic Heat for CH_4')
title('Specfic Heat Capcity at Constat Pressure for CH_4','FontSize',12)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a = get(handles.input1,'String');
b = get(handles.input2,'String');
c = get(handles.input3,'String');
d = get(handles.input4,'String');
e = get(handles.input5,'String');
f = get(handles.input6,'String');
g = get(handles.input7,'String');
h = get(handles.input8,'String');
i = get(handles.input9,'String');
j = get(handles.input10,'String');
set(handles.input1,'String',0);
set(handles.input2,'String',0);
set(handles.input3,'String',0);
set(handles.input4,'String',0);
set(handles.input5,'String',0);
set(handles.input6,'String',0);
set(handles.input7,'String',0);
set(handles.input8,'String',0);
set(handles.input9,'String',0);
set(handles.input10,'String',0);
guidata(hObject, handles);
clc
clear
cla
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
A1 = get(handles.input1,'String');
A2 = get(handles.input2,'String');
A3 = get(handles.input3,'String');
A4 = get(handles.input4,'String');
A5 = get(handles.input5,'String');
A6 = get(handles.input6,'String');
tMIN = get(handles.input7,'String');
tMAX = get(handles.input8,'String');
M = get(handles.input9,'String');
Molecular_Weight = get(handles.input10,'String');
set(handles.input1,'String',-0.29149);
set(handles.input2,'String',26.327);
set(handles.input3,'String',-10.610);
set(handles.input4,'String',1.5656);
set(handles.input5,'String',0.16573);
set(handles.input6,'String',-18.33);
set(handles.input7,'String',-15.1500);
set(handles.input8,'String',900);
set(handles.input9,'String',1000);
set(handles.input10,'String',16);
guidata(hObject,handles)
TMIN=273+tMIN;
TMAX=273+tMAX;
dt=(TMAX-TMIN)/M;
Dt(1)=TMIN;
for i=1:M+1;
Dt(i+1)=Dt(i)+dt;
TH(i)=Dt(i+1)/1000;
CP(i)=4.184*(A1+A2*TH(i)+A3*(TH(i))^2+A4*(TH(i))^3+A5*(TH(i))^-2)/16;
end
T=(TMIN:dt:TMAX);
% Store the data in handles as a structure to be able to access it globally
% from other functions
handles.CP=CP;
handles.T=T;
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
A1 = get(handles.input1,'String');
A2 = get(handles.input2,'String');
A3 = get(handles.input3,'String');
A4 = get(handles.input4,'String');
A5 = get(handles.input5,'String');
A6 = get(handles.input6,'String');
tMIN = get(handles.input7,'String');
tMAX = get(handles.input8,'String');
M = get(handles.input9,'String');
Molecular_Weight = get(handles.input10,'String');
TMIN=273+str2num(tMIN);
TMAX=273+str2num(tMAX);
dt=(TMAX-TMIN)/str2num(M);
Dt(1)=TMIN;
for i=1:str2num(M)+1;
Dt(i+1)=Dt(i)+dt;
TH(i)=Dt(i+1)/1000;
CP(i)=4.184*(str2num(A1)+str2num(A2)*TH(i)+str2num(A3)*(TH(i))^2+str2num(A4)*(TH(i))^3+str2num(A5)*(TH(i))^-2)/str2num(Molecular_Weight);
end
T=(TMIN:dt:TMAX);
handles.CP=CP;
handles.T=T;
guidata(hObject,handles)
You can downlaod the Code by pressing on the picture:
You can downlaod the template by pressing on the picture:
Unless otherwise noted, all content on this site is @Copyright by Ahmed Al Makky 2012-2013 - http://cfd2012.com